Here’s a simple breakdown of the main cost items you should be aware of.
1. Value-added tax product value
Product value is the foundation of your landing cost. Always check whether the price includes taxes and other fees to avoid being double-charged.
2. Mass Production Inspection
Before shipping, it’s crucial to inspect the product quality to ensure it meets the agreed-upon standards. You can either hire a third-party inspector or request that the factory conduct the inspection. Just be sure to account for the additional cost if you choose to go with a third-party inspection.
3. Export Customs Clearance & Duty
It’s essential to clarify which party is responsible for export customs clearance and payment of duties. If you’re not familiar with the process, it’s advisable to have the seller handle it or work with an experienced freight forwarder. If you’re responsible for these costs, be sure to factor them into your budget.
4. Inland Transport
This involves transporting goods from the factory to the export port, encompassing trucking, local handling, and export documentation. This is the most forgettable cost that might be mis-calculated.
5. International Shipping
The main journey from one country to another is usually by sea, air, or rail. Freight cost depends on shipment size, weight, and distance. Normally, the lower the cost, the longer it will take. Choosing a port that is big and close to your warehouse location will save money on transport.
6. Import Customs Clearance & Duty
Every country has import regulations and taxes (or duties) based on the type of product and its value. Import customs clearance is the process of officially bringing your goods into the country. During the quotation, you need to figure out which party is in charge of it.
7. Port to the warehouse
After your goods arrive at the port of import, they still need to be transported to your warehouse, store, or customer’s location.
8. Lab Testing
Some products (especially kitchenware, toys, or electronics) need safety or compliance testing to meet local standards — such as FDA, CE, or LFGB certifications. Consult with the professionals to obtain the accurate price.
9. Artwork & Packaging Costs
Designing packaging, printing labels, and creating logos or color boxes all have setup costs, especially for custom designs.
10. Other Costs
Additionally, there are other costs, such as specific export documentation required to clear goods at customs.
How do we make sure which part is included in the quotation?
You can find 4 factors in the quotation for each product. Currency, price, unit, and Incoterms. Each factor is essential. The cost and risks are based on the Incoterms you selected. Below is a table to define the point at which the costs and risks of the transaction transfer from the seller to your warehouse.
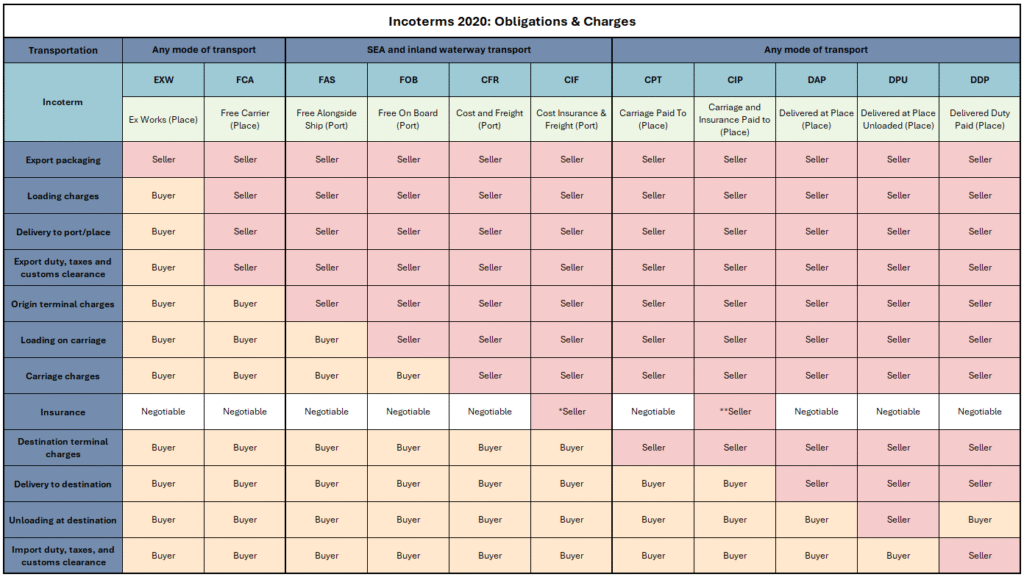
Apply to any mode or modes of transport
EXW: The seller only includes the product value and packing cost. The risk and cost will transfer to the buyer once the loading operation occurs. The buyer will bear the cost of loading the goods on any collecting vehicle. The place of delivery does not necessarily have to be the seller’s premises.
FCA: The seller delivers the goods to a mutually agreed location. If that location is the seller’s premises, delivery occurs when the goods are loaded onto the buyer’s transport. If it’s another location, delivery occurs when the goods are placed at the buyer’s disposal on the seller’s transport, ready for unloading. At this delivery point, risk and costs transfer to the buyer. The seller handles export clearance, so the buyer doesn’t bear the costs or risks associated with export.
CPT: The seller completes the delivery and transfers risk to the buyer in the following ways:
- Delivering the goods to the carrier.
- contracted by the seller
- or by procuring the goods so delivered.
- The seller may do so by giving the carrier physical possession of the goods in the manner and at the place appropriate to the means of transport used.
The risk transfers from seller to buyer when the goods are delivered to the buyer by handing them over to the carrier. But the seller should bear the transfer cost to the destination. This means that in this term, two locations are important, the place where the goods are delivered and the place agreed as the destination.
CIP: Compared to CPT, CIP requires the seller to arrange insurance coverage for the buyer’s risk of loss or damage to the goods from the point of delivery to the destination. Normally, the insurance coverage amount is calculated at 110% of the invoice amount.
DAP: The seller must deliver the goods by placing them at the disposal of the buyer on the arriving means of transport ready for unloading at the agreed point, if any, at the named place of destination or by procuring the goods so delivered. Once goods are delivered, all costs (including unloading) and risks are transferred to the buyer.
DPU: Compared to DAP, DPU requires the seller to unload the goods at the delivery place. The buyer must clear the goods for import and bear the associated import costs.
DDP: The costs before that place or point of delivery/destination are for the account of the seller, including the costs of import clearance, and the costs after that place or point, other than the costs of import, are for the account of the buyer. The buyer also needs to pay the unloading cost.
Apply only to sea and inland waterway transport
FAS: The buyer must pay all costs related to the goods from the time when the goods are placed alongside the ship. Export clearance must be taken charge of by the seller.
FOB: The buyer must pay all costs relating to the goods from the time they have been placed on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the loading point, if any, indicated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
CFR: Compared to FOB, CFR requires the seller to pay for the costs of transit and clear the goods for export. The point that needs to be paid attention to is that the risks are transferred to the buyer since they have been placed on board the vessel nominated by the buyer at the loading point, if any, indicated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
CIF: The cost for CIF for the buyer is the same as CFR. The difference is that CIF requires the seller to contract for insurance to cover the buyer’s risk of loss or damage to the goods from the port of shipment to at less the port of destination.
In summary, import and export costs go beyond just the product price. It’s crucial to account for additional expenses like taxes, inspections, customs duties, and transport fees. By carefully reviewing quotes and understanding Incoterms, you can clarify which costs and risks are yours to manage. Partnering with experienced freight forwarders or customs brokers can help streamline the process and ensure smooth transactions. With proper planning, you can effectively manage these costs and build a strong foundation for your international business.
Reference: https:iccwbo.org